3D Printing as useful tool in casting custom door handles
Casting a custom door handle requires an understanding of the shrinkage that occurs in traditional lost wax casting. When casting in bronze or steel the process starts with a pattern often sculpted by hand in wood or clay but with the advent of 3D printing we are now in some cases able to produce this as a Quick Cast stereolithographic print (SLA). While these 3D prints are useful in developing prototypes they still need to be finished by hand and are often too expensive to be used as wax substitutes since they too are burnt out and wasted in the lost wax process.
3D prints have their place as prototypes and for custom short run projects where the cost of developing a mold or tooling cannot be amortized over a large enough quantity to make the project cost effective.
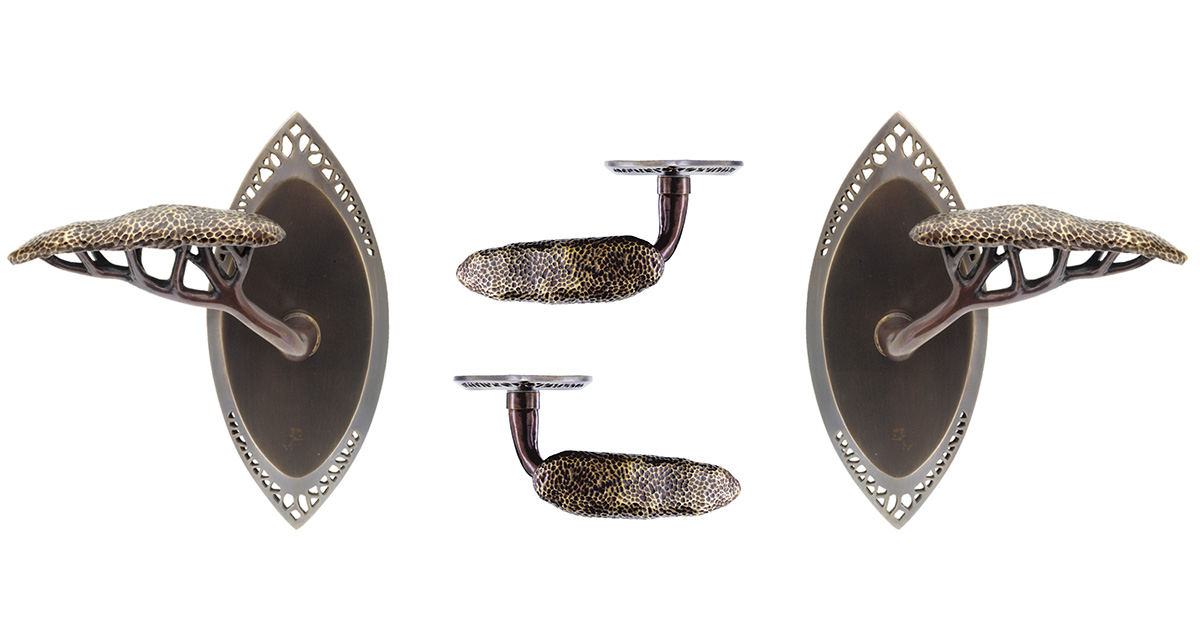
Recently we considered 3D printing as a protype tool in helping to create a left and right pattern for a short run project of 4 sets of door handles. When developing a new handle set we often break the design down into component parts and where there is a directional detail this means we must make 2 patterns one for left and one for the right facing section. 3D scanning and modeling allows us to use one carved pattern to create a second mirror image model that is printed in a resin compound. While this reduces the development cost, the digital print often needs to be re-carved so that very fine details like leaf veins and scales can be sharpened by hand.
The picture below of the Hedgerow door lever shows that the branches of this piece are very directional thus requiring a left and right mold, but the canopy is generic to both levers.
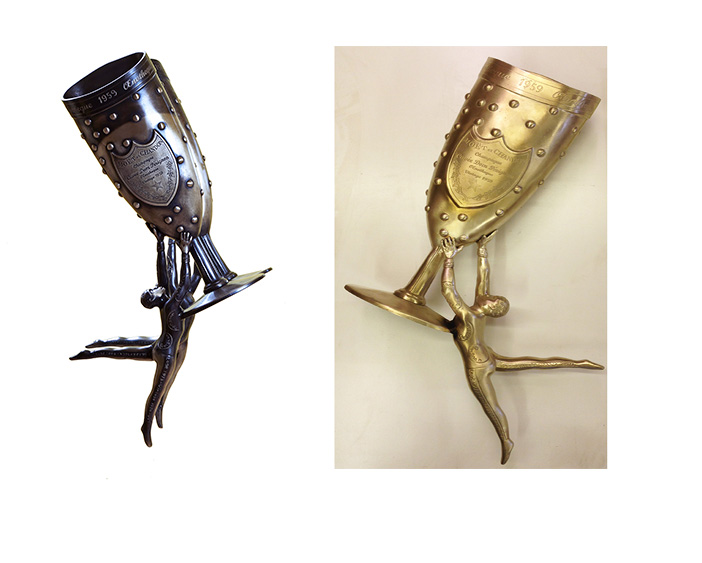
One advantage that SLA’s have over wax patterns is that they are not subject to shrinkage. In lost wax casting shrinkage occurs when the molten wax solidifies and when the bronze or steel casting is poured. There are a wide variety of waxes used in this process and their composition effects how they pour, how they solidify and how much they shrink. While a wax pattern may shrink by approximately .6% no shrinkage occurs with the print.
Trying to mathematically predict the exact amount by which the wax pattern and subsequent casting will shrink is difficult when developing a new piece. If the dimension of the piece is critical then we will often create a mold and wax of a smaller section so that we can exactly determine the overall shrinkage and can then re-scale the complete piece making it and the subsequent mold large enough to compensate for this shrinkage.